Textile industry
The textile industry in transition
Historically, textile and clothing companies were at the forefront of the Industrial Revolution.
The textile industry is one of the oldest and, in terms of number of employees and revenue, one of the most important sectors of the manufacturing industry. It encompasses a wide variety of different products, which can be summarized under the following categories: clothing and fashion, home textiles, and technical textiles.
Despite slightly declining economic indicators for the textile industry in Germany, the "technical textiles" sub-sector is experiencing economic and employment growth and will establish itself as a high-tech segment in the structural transformation of the textile industry. More than 50 percent of the textiles produced in Germany are technical textiles. These textiles are used, for example, in lightweight textile construction (insulation, roof structures, bridge construction), in the healthcare sector (wound dressings, personal protective equipment), and in the automotive sector (airbags, protective casings for the engines of electric vehicles).

Until now, automation had left textile manufacturing more or less untouched – but that is now changing.
Automation in textile production
In the textile industry, as many processes as possible need to be automated to meet exponentially growing demand. The problem is that this industry uses many different types of machines, so flexibility and ease of installation are crucial.
By using advanced technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and automated production lines, companies can optimize their production processes and increase efficiency. Automated machines can perform tasks such as weaving, knitting, dyeing, and cutting, resulting in faster and more precise production. Furthermore, automated inspection systems can help improve textile quality by detecting and sorting out defects and errors early on. Automation also enables companies to respond to individual customer requests and offer customized textile products.

Sustainability
The textile industry is under growing pressure to produce more environmentally friendly and operate more sustainably. Automation can play a key role in supporting this transformation. Through the targeted use of automated systems, production processes can be made not only more efficient but also more resource-efficient.
Modern production facilities enable more precise dosing of materials, reducing consumption while improving quality. Waste can also be significantly reduced in this way.
Another important area is the careful use of water and energy. Automatic systems for water treatment or energy consumption control help minimize environmental impact – often while also reducing operating costs.
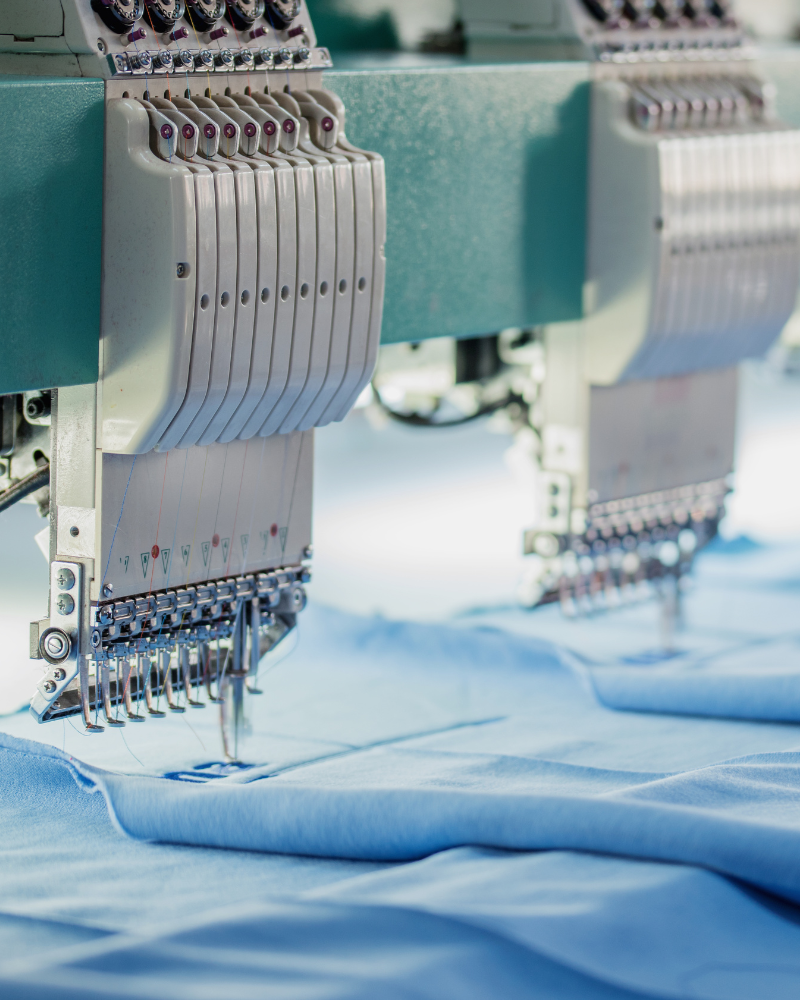

Increased efficiency
Automation brings numerous benefits to the textile industry – particularly in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Through the targeted use of automated machines and digitally controlled processes, companies can significantly increase their production capacities while simultaneously shortening lead times. This allows products to be brought to market faster, enabling a more flexible response to changing customer needs and market requirements.
Another key benefit is improved product quality. Automated systems operate with high precision and consistent reliability, largely eliminating human error. This leads to more consistent results, less waste, and overall higher-quality textiles.
The need for manual labor can be reduced, especially for repetitive or physically demanding tasks. At the same time, material consumption is managed more efficiently.